1971. 寻找图中是否存在路径
1971. 寻找图中是否存在路径
有一个具有 n 个顶点的 双向 图,其中每个顶点标记从 0 到 n - 1(包含 0 和 n - 1)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示顶点 ui 和顶点 vi 之间的双向边。 每个顶点对由 最多一条 边连接,并且没有顶点存在与自身相连的边。
请你确定是否存在从顶点 source 开始,到顶点 destination 结束的 有效路径 。
给你数组 edges 和整数 n、source 和 destination,如果从 source 到 destination 存在 有效路径 ,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
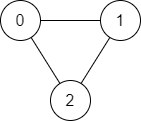
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:true
解释:存在由顶点 0 到顶点 2 的路径:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
示例 2:
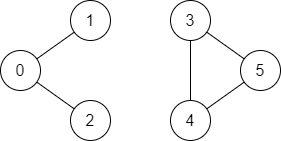
输入:n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
输出:false
解释:不存在由顶点 0 到顶点 5 的路径.
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1不存在重复边
不存在指向顶点自身的边
官方题解
使用深度优先搜索检测顶点 source,destination的连通性,需要从顶点 source开始依次遍历每一条可能的路径,判断可以到达顶点 destination,同时还需要记录每个顶点的访问状态防止重复访问。
首先从顶点 source 开始遍历并进行递归搜索。搜索时每次访问一个顶点 vertex 时,如果 vertex 等于 destination 则直接返回,否则将该顶点设为已访问,并递归访问与 vertex 相邻且未访问的顶点 next。如果通过 next 的路径可以访问到 destination,此时直接返回 true,当访问完所有的邻接节点仍然没有访问到 destination,此时返回 false。
深度优先
class Solution {
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
List<Integer>[] adj = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int x = edge[0], y = edge[1];
adj[x].add(y);
adj[y].add(x);
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
return dfs(source, destination, adj, visited);
}
public boolean dfs(int source, int destination, List<Integer>[] adj, boolean[] visited) {
if (source == destination) {
return true;
}
visited[source] = true;
for (int next : adj[source]) {
if (!visited[next] && dfs(next, destination, adj, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
